Far too much of our thinking tends to look at immediate results. In the case of this issue, long term thinking is very powerful. Read the following essay on what is happening long term in our culture in regard to sexual mores.
Sex After Christianity, By Rod Dreher (source)
Twenty years ago, new president Bill Clinton stepped on a political landmine when he tried to fulfill a campaign promise to permit gay soldiers to serve openly. Same-sex marriage barely registered as a political cause; the country was then three years away from the Defense of Marriage Act and four years from comedian Ellen DeGeneres’s prime-time coming out.
Then came what historians will one day recall as a cultural revolution. Now we’re entering the endgame of the struggle over gay rights and the meaning of homosexuality. Conservatives have been routed, both in court and increasingly in the court of public opinion. It is commonly believed that the only reason to oppose same-sex marriage is rank bigotry or for religious reasons, neither of which—the argument goes—has any place in determining laws or public standards.
The magnitude of the defeat suffered by moral traditionalists will become ever clearer as older Americans pass from the scene. Poll after poll shows that for the young, homosexuality is normal and gay marriage is no big deal—except, of course, if one opposes it, in which case one has the approximate moral status of a segregationist in the late 1960s.
All this is, in fact, a much bigger deal than most people on both sides realize, and for a reason that eludes even ardent opponents of gay rights. Back in 1993, a cover story in The Nation identified the gay-rights cause as the summit and keystone of the culture war:
All the crosscurrents of present-day liberation struggles are subsumed in the gay struggle. The gay moment is in some ways similar to the moment that other communities have experienced in the nation’s past, but it is also something more, because sexual identity is in crisis throughout the population, and gay people—at once the most conspicuous subjects and objects of the crisis—have been forced to invent a complete cosmology to grasp it. No one says the changes will come easily. But it’s just possible that a small and despised sexual minority will change America forever.
They were right, and though the word “cosmology” may strike readers as philosophically grandiose, its use now appears downright prophetic. The struggle for the rights of “a small and despised sexual minority” would not have succeeded if the old Christian cosmology had held: put bluntly, the gay-rights cause has succeeded precisely because the Christian cosmology has dissipated in the mind of the West.
Same-sex marriage strikes the decisive blow against the old order. The Nation’s triumphalist rhetoric from two decades ago is not overripe; the radicals appreciated what was at stake far better than did many—especially bourgeois apologists for same-sex marriage as a conservative phenomenon. Gay marriage will indeed change America forever, in ways that are only now becoming visible. For better or for worse, it will make ours a far less Christian culture. It already is doing exactly that.
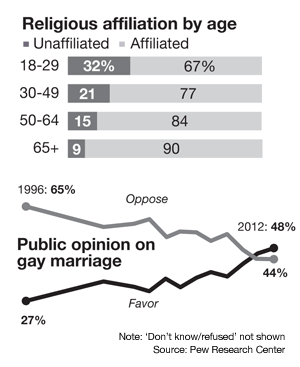
When they were writing the widely acclaimed 2010 book American Grace, a comprehensive study of contemporary religious belief and practice, political scientists Robert D. Putnam and David E. Campbell noticed two inverse trend lines in social-science measures, both starting around 1990.
They found that young Americans coming into adulthood at that time began to accept homosexuality as morally licit in larger numbers. They also observed that younger Americans began more and more to fall away from organized religion. The evangelical boom of the 1970s and 1980s stopped, and if not for a tsunami of Hispanic immigration the U.S. Catholic church would be losing adherents at the same rate as the long-dwindling Protestant mainline.
Over time, the data showed, attitudes on moral issues proved to be strong predictors of religious engagement. In particular, the more liberal one was on homosexuality, the less likely one was to claim religious affiliation. It’s not that younger Americans were becoming atheists. Rather, most of them identify as “spiritual, but not religious.” Combined with atheists and agnostics, these “Nones”—the term is Putnam’s and Campbell’s—comprise the nation’s fastest-growing faith demographic.
Indeed, according to a 2012 Pew Research Center study, the Nones comprise one out of three Americans under 30. This is not simply a matter of young people doing what young people tend to do: keep church at arm’s length until they settle down. Pew’s Greg Smith told NPR that this generation is more religiously unaffiliated than any on record. Putnam—the Harvard scholar best known for his best-selling civic culture study Bowling Alone—has said that there’s no reason to think they will return to church in significant numbers as they age.
Putnam and Campbell were careful to say in American Grace that correlation is not causation, but they did point out that as gay activism moved toward center stage in American political life—around the time of The Nation’s cover story—the vivid public role many Christian leaders took in opposing gay rights alienated young Americans from organized religion.
In a dinner conversation not long after the publication of American Grace, Putnam told me that Christian churches would have to liberalize on sexual teaching if they hoped to retain the loyalty of younger generations. This seems at first like a reasonable conclusion, but the experience of America’s liberal denominations belies that prescription. Mainline Protestant churches, which have been far more accepting of homosexuality and sexual liberation in general, have continued their stark membership decline.
It seems that when people decide that historically normative Christianity is wrong about sex, they typically don’t find a church that endorses their liberal views. They quit going to church altogether.
This raises a critically important question: is sex the linchpin of Christian cultural order? Is it really the case that to cast off Christian teaching on sex and sexuality is to remove the factor that gives—or gave—Christianity its power as a social force?
Though he might not have put it quite that way, the eminent sociologist Philip Rieff would probably have said yes. Rieff’s landmark 1966 book The Triumph Of the Therapeutic analyzes what he calls the “deconversion” of the West from Christianity. Nearly everyone recognizes that this process has been underway since the Enlightenment, but Rieff showed that it had reached a more advanced stage than most people—least of all Christians—recognized.
Rieff, who died in 2006, was an unbeliever, but he understood that religion is the key to understanding any culture. For Rieff, the essence of any and every culture can be identified by what it forbids. Each imposes a series of moral demands on its members, for the sake of serving communal purposes, and helps them cope with these demands. A culture requires a cultus—a sense of sacred order, a cosmology that roots these moral demands within a metaphysical framework.
You don’t behave this way and not that way because it’s good for you; you do so because this moral vision is encoded in the nature of reality. This is the basis of natural-law theory, which has been at the heart of contemporary secular arguments against same-sex marriage (and which have persuaded no one).
Rieff, writing in the 1960s, identified the sexual revolution—though he did not use that term—as a leading indicator of Christianity’s death as a culturally determinative force. In classical Christian culture, he wrote, “the rejection of sexual individualism” was “very near the center of the symbolic that has not held.” He meant that renouncing the sexual autonomy and sensuality of pagan culture was at the core of Christian culture—a culture that, crucially, did not merely renounce but redirected the erotic instinct. That the West was rapidly re-paganizing around sensuality and sexual liberation was a powerful sign of Christianity’s demise.
It is nearly impossible for contemporary Americans to grasp why sex was a central concern of early Christianity. Sarah Ruden, the Yale-trained classics translator, explains the culture into which Christianity appeared in her 2010 book Paul Among The People. Ruden contends that it’s profoundly ignorant to think of the Apostle Paul as a dour proto-Puritan descending upon happy-go-lucky pagan hippies, ordering them to stop having fun.
In fact, Paul’s teachings on sexual purity and marriage were adopted as liberating in the pornographic, sexually exploitive Greco-Roman culture of the time—exploitive especially of slaves and women, whose value to pagan males lay chiefly in their ability to produce children and provide sexual pleasure. Christianity, as articulated by Paul, worked a cultural revolution, restraining and channeling male eros, elevating the status of both women and of the human body, and infusing marriage—and marital sexuality—with love.
Christian marriage, Ruden writes, was “as different from anything before or since as the command to turn the other cheek.” The point is not that Christianity was only, or primarily, about redefining and revaluing sexuality, but that within a Christian anthropology sex takes on a new and different meaning, one that mandated a radical change of behavior and cultural norms. In Christianity, what people do with their sexuality cannot be separated from what the human person is.
It would be absurd to claim that Christian civilization ever achieved a golden age of social harmony and sexual bliss. It is easy to find eras in Christian history when church authorities were obsessed with sexual purity. But as Rieff recognizes, Christianity did establish a way to harness the sexual instinct, embed it within a community, and direct it in positive ways.
What makes our own era different from the past, says Rieff, is that we have ceased to believe in the Christian cultural framework, yet we have made it impossible to believe in any other that does what culture must do: restrain individual passions and channel them creatively toward communal purposes.
Rather, in the modern era, we have inverted the role of culture. Instead of teaching us what we must deprive ourselves of to be civilized, we have a society that tells us we find meaning and purpose in releasing ourselves from the old prohibitions.
How this came to be is a complicated story involving the rise of humanism, the advent of the Enlightenment, and the coming of modernity. As philosopher Charles Taylor writes in his magisterial religious and cultural history A Secular Age, “The entire ethical stance of moderns supposes and follows on from the death of God (and of course, of the meaningful cosmos).” To be modern is to believe in one’s individual desires as the locus of authority and self-definition.
Gradually the West lost the sense that Christianity had much to do with civilizational order, Taylor writes. In the 20th century, casting off restrictive Christian ideals about sexuality became increasingly identified with health. By the 1960s, the conviction that sexual expression was healthy and good—the more of it, the better—and that sexual desire was intrinsic to one’s personal identity culminated in the sexual revolution, the animating spirit of which held that freedom and authenticity were to be found not in sexual withholding (the Christian view) but in sexual expression and assertion. That is how the modern American claims his freedom.
To Rieff, ours is a particular kind of “revolutionary epoch” because the revolution cannot by its nature be institutionalized. Because it denies the possibility of communal knowledge of binding truths transcending the individual, the revolution cannot establish a stable social order. As Rieff characterizes it, “The answer to all questions of ‘what for’ is ‘more’.”
Our post-Christian culture, then, is an “anti-culture.” We are compelled by the logic of modernity and the myth of individual freedom to continue tearing away the last vestiges of the old order, convinced that true happiness and harmony will be ours once all limits have been nullified.
Gay marriage signifies the final triumph of the Sexual Revolution and the dethroning of Christianity because it denies the core concept of Christian anthropology. In classical Christian teaching, the divinely sanctioned union of male and female is an icon of the relationship of Christ to His church and ultimately of God to His creation. This is why gay marriage negates Christian cosmology, from which we derive our modern concept of human rights and other fundamental goods of modernity. Whether we can keep them in the post-Christian epoch remains to be seen.
It also remains to be seen whether we can keep Christianity without accepting Christian chastity. Sociologist Christian Smith’s research on what he has termed “moralistic therapeutic deism”—the feel good, pseudo-Christianity that has supplanted the normative version of the faith in contemporary America—suggests that the task will be extremely difficult.
Conservative Christians have lost the fight over gay marriage and, as we have seen, did so decades before anyone even thought same-sex marriage was a possibility. Gay-marriage proponents succeeded so quickly because they showed the public that what they were fighting for was consonant with what most post-1960s Americans already believed about the meaning of sex and marriage. The question Western Christians face now is whether or not they are going to lose Christianity altogether in this new dispensation.
Too many of them think that same-sex marriage is merely a question of sexual ethics. They fail to see that gay marriage, and the concomitant collapse of marriage among poor and working-class heterosexuals, makes perfect sense given the autonomous individualism sacralized by modernity and embraced by contemporary culture—indeed, by many who call themselves Christians. They don’t grasp that Christianity, properly understood, is not a moralistic therapeutic adjunct to bourgeois individualism—a common response among American Christians, one denounced by Rieff in 2005 as “simply pathetic”—but is radically opposed to the cultural order (or disorder) that reigns today.
They are fighting the culture war moralistically, not cosmologically. They have not only lost the culture, but unless they understand the nature of the fight and change their strategy to fight cosmologically, within a few generations they may also lose their religion.
“The death of a culture begins when its normative institutions fail to communicate ideals in ways that remain inwardly compelling,” Rieff writes. By that standard, Christianity in America, if not American spirituality, is in mortal danger. The future is not foreordained: Taylor shares much of Rieff’s historical analysis but is more hopeful about the potential for renewal. Still, if the faith does not recover, the historical autopsy will conclude that gay marriage was not a cause but a symptom, the sign that revealed the patient’s terminal condition.